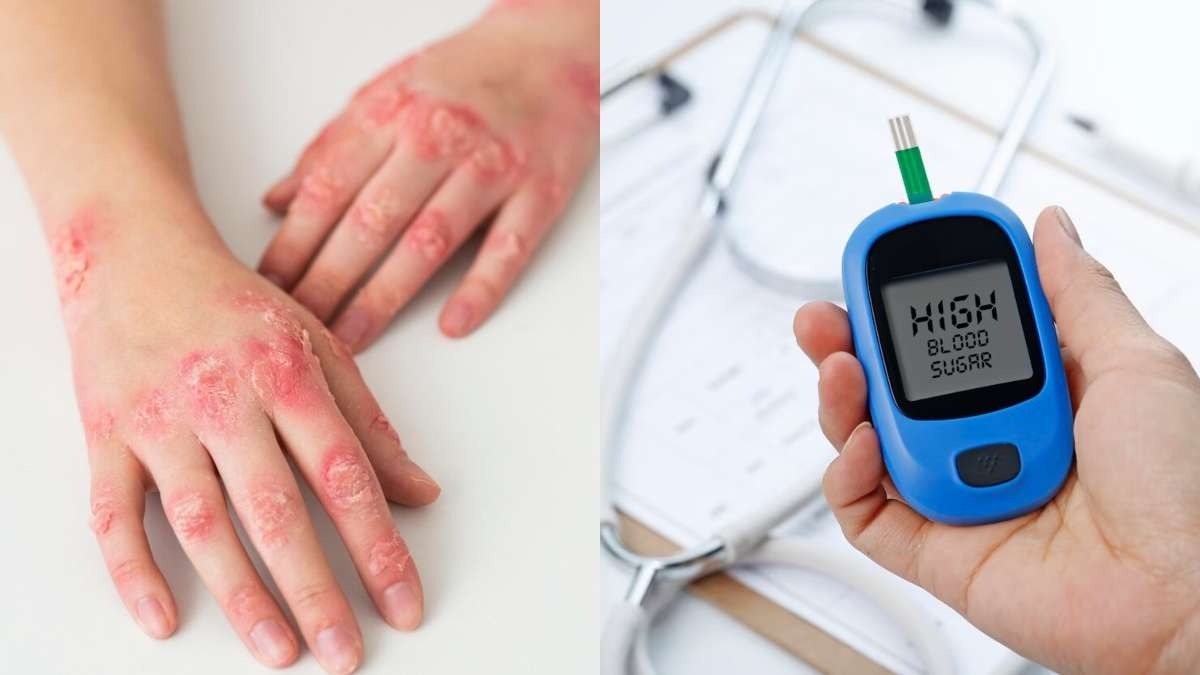
Health: Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can affect diabetic patients. It is a result of poor blood flow and nerve damage, making it difficult for the body to fight off infections. Gangrene can spread rapidly if not diagnosed and treated early. To diagnose gangrene in diabetic patients, one must know about the factors that cause it.
Gangrene can spread rapidly in diabetes patients due to several factors mentioned by Dr Kundan Khamkar MBBS MD, Medicine, Ruby Hall Clinic, Pune:-
- Poor Blood Circulation: Diabetes often leads to peripheral artery disease, reducing blood flow to extremities.
- Neuropathy: Diabetic neuropathy can cause reduced sensation, making patients unaware of injuries or infections.
- Wound Healing Impairment: Elevated blood sugar levels can inhibit the body's natural healing processes.
- Weakened Immune System: Diabetes can compromise the immune response, making it harder to fight infections.
- Infection Risk: High glucose levels can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth, increasing the risk of infections.
These factors collectively exacerbate the risk of gangrene in individuals with diabetes.
Effective ways to diagnose gangrene in diabetic patients can be achieved through.
- Regular Foot Examinations: Routine checks for cuts, blisters, and discolouration.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Awareness of signs such as increased pain, swelling, or foul-smelling discharge.
- Skin Temperature Checks: Comparing warmth between limbs can indicate circulation issues.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasounds or MRIs may be utilised to assess blood flow and tissue viability.
- Blood Tests: Checking for signs of infection or elevated glucose levels.
Prompt identification of symptoms and continuous monitoring can aid in early diagnosis.
If gangrene is suspected, immediate steps include:-
- Seek Medical Attention: Early intervention is crucial.
- Do Not Apply Heat or Ice: This may worsen tissue damage.
- Keep the Area Clean: Cover with a sterile dressing to prevent further infection.
- Elevate Affected Limb: This can help reduce swelling.
- Avoid Self-Treatment: Professional evaluation and intervention are necessary for proper care.
Management should involve healthcare professionals to prevent severe outcomes.
To reduce the risk of gangrene and other complications, consider these strategies:-
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Keep glucose levels within the target range.
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a well-balanced diet to maintain optimal weight and blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to improve circulation and overall health.
- Foot Care: Regularly inspect feet, maintain hygiene, and visit a podiatrist for professional care.
- Medication Compliance: Adhere to prescribed medications for diabetes management and any additional treatments.
Comprehensive care can significantly lower the risk of serious complications.
Available treatments for gangrene include:-
- Surgical Debridement: Removal of dead or infected tissue to prevent further spread.
- Antibiotics: Prescribing appropriate antibiotics based on the infection type.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: This can enhance oxygenation to tissues, promoting healing.
- Wound Care Management: Using advanced dressings and therapies to encourage recovery.
- Possible Amputation: In severe cases where tissue death is extensive.
Ensuring coordinated care with healthcare professionals can optimize treatment outcomes and minimise complications.
--Advertisement--

 Desk
Desk Share
Share






